|
Noninvasive Real-Time Recording of Cardiac Conduction System Activity.
Instrumentation and
Method Used in QRS-Triggered Averaging. W. Wajszczuk, T. Palko, M.J.
Stopczyk, T. Bauld, M.S. Moskowitz, J. Przybylski, R.J. Zochowski, and
M. Rubenfire. Non-invasive Cardiovascular Diagnosis – Current
Concepts, Edited by Edward B. Dietrich, Chapter 35, pp.
337-359, Copyright 1978, University Park Press, Baltimore.

His Bundle
Other Publications:
Noninvasive recording of His-Purkinje
activity in man by ORS-triggered signal averaging. Wajszczuk WJ,
Stopczyk MJ, Moskowitz MS, Zochowski RJ, Bauld T, Dabos PL, Rubenfire
M. Circulation. 1978 Jul; 58(1):95-102.
(http://www.labmeeting.com/papers/author/wajszczuk-w
)
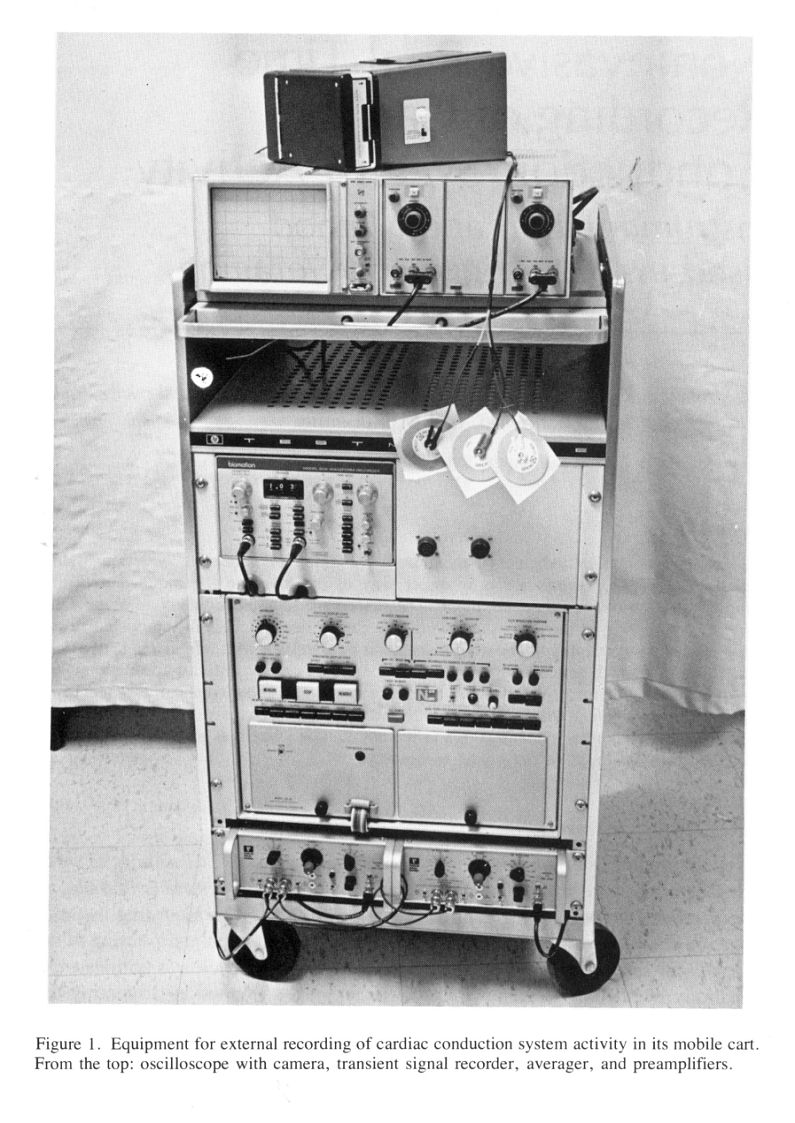
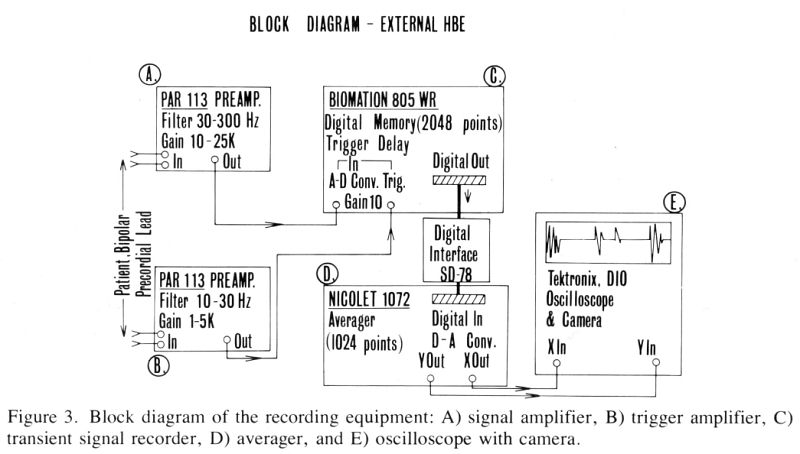
Mobile instrumentation and
a clinically applicable method have been developed for external His
bundle recording. High gain signal amplification
105 filtering (30--300 Hz) and averaging (128 or 256
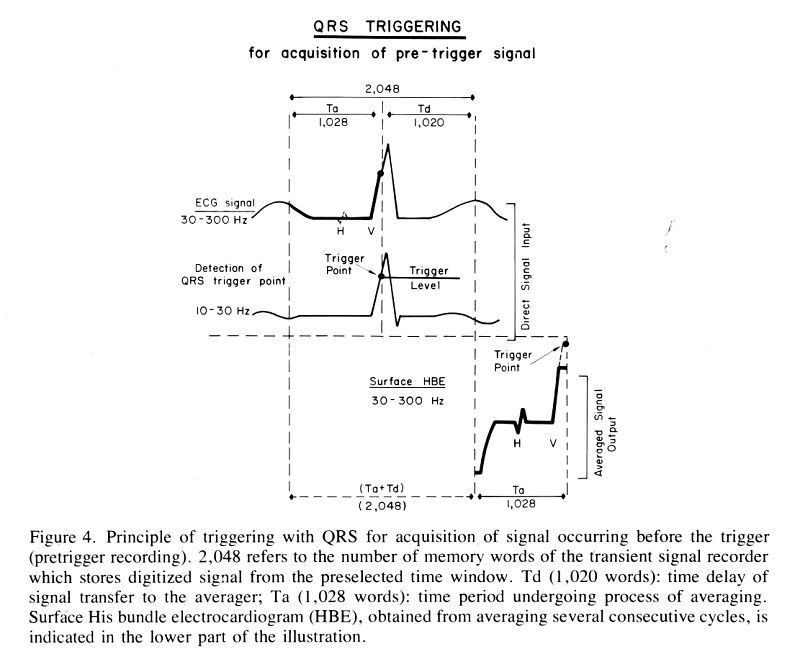
consecutive cycles) are used. Acquisition of signals arising in the
P-R interval is triggered by the patient's QRS signal at the end of
that interval. The precordial bipolar electrocardiogram is digitized
at 5k HZ with 8 bit resolution and transferred to a 1,024 word, 18 bit
signal averager. The averaged signal is then displayed on an
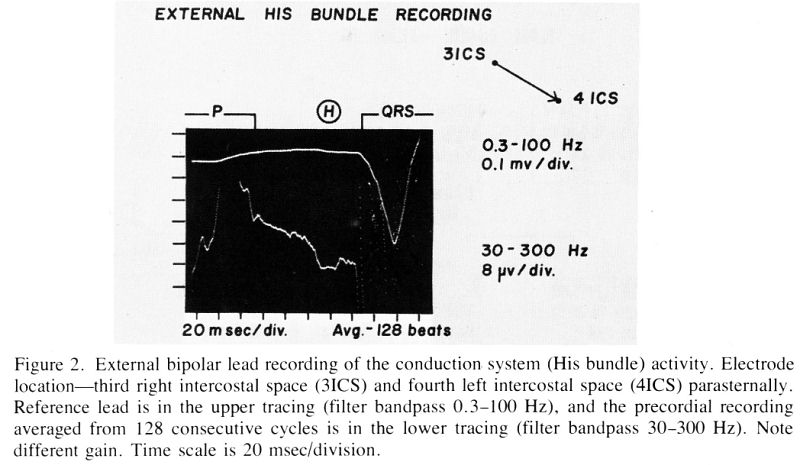
oscilloscope and photographed. Good correlations were obtained between
direct intracardiac and precordial recordings in experimental animals
and in humans. Noise level after averaging was below 0.3
μV and there was good
elimination of asynchronous atrial and ectopic ventricular activity.
With averaging of 128 or 256 consecutive cycles, the signal
attenuation after propagation to the chest wall was in the range
1:2000 to 1:4000 in comparison with the directly recorded His bundle
activity deflections. The noninvasive method may be of value in
follow-up of acute and chronic disturbances of atrioventricular
conduction, as well as in studies of effects of pharmacologic
interventions.
Noninvasive
external recording of cardiac conduction system (His bundle) activity.
Wajszczuk WJ,
Moskowitz MS, Bauld T, Dabos P, Weiss R, Rubenfire M.
Med Instrum.
1978, Sep-Oct;12(5):282-7.
http://www.labmeeting.com/papers/author/wajszczuk-w
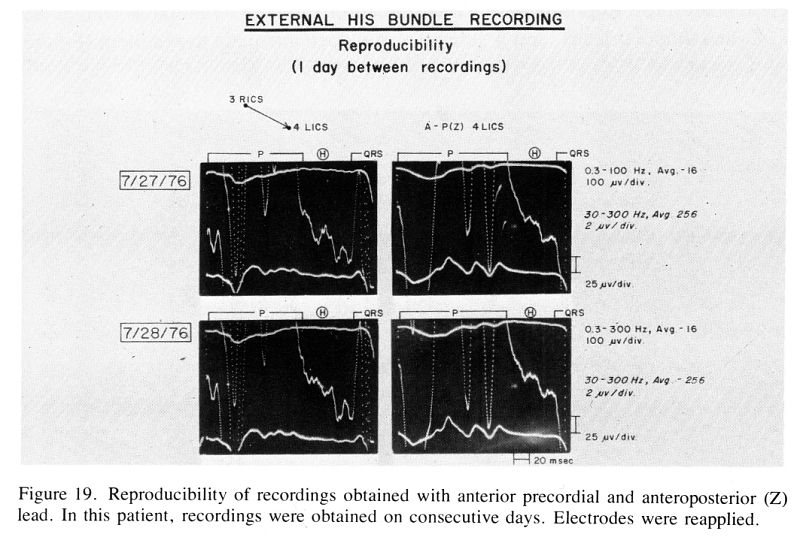
Successful and adequate
external recording of the cardiac conduction system from the body's
surface can be accomplished in 80 to 90 percent of subjects studied.
High-gain amplification, signal averaging, and triggering with a
conditioned QRS signal results in good recording reproducibility.
Averaging of 128 consecutive cycles is adequate, but on occasion
averaging of 256 cycles may yield better results. The patients's QRS
signal triggers the transfer of signals, which are digitized and
stored during the preceding P-R interval. Comparison of external
recordings with direct invasive recordings in animals and patients
shows good correlation between the major His bundle deflections. The
advantages of the system developed include its mobility, triggering
the QRS with pre-trigger data processing, and instantaneous display on
Polaroid photograph. Future research should concentrate on further
miniaturization and simplification of the instrumentation, detailed
experimental comparison between direct and external recordings for
identification of deflections and their origin, further study of the
recording lead system, and the most appropriate method of information
display.
Pre-P (Sinus
Node Region)
Sinus
node activity in man and animal studies recorded intraatrially by an
on-line pre-memorized averaging technique.
Mariusz J. Stopczyk, Marian
Pieniak, Waldemar J. Wajszczuk and Melvyn Rubenfire.
Excerpta Medica
International Congress Series No. 395.
CARDIAC PACING, Proceedings of the Vth International Symposium, Tokyo,
March 14-18, 1976, pp. 13-18.
Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam,
ISBN 90 219 0326 1.
Summary
A
method for precordial His bundle potential recordings recently
developed in our laboratory was adapted for the visualization of
sinoatrial (SA) node activity. The method includes high-gain
amplification, filtering and averaging of the pre-memorized
post-triggered signal. Potentials for averaging were recorded with a
unipolar intraatrial lead with distant electrode located in a large
venous vessel. A bipolar intraatrial recording (A wave deflection) was
used as a trigger. Final recordings were obtained from averaging of up
to 1,024 sinus beats and photographed from the oscilloscope.
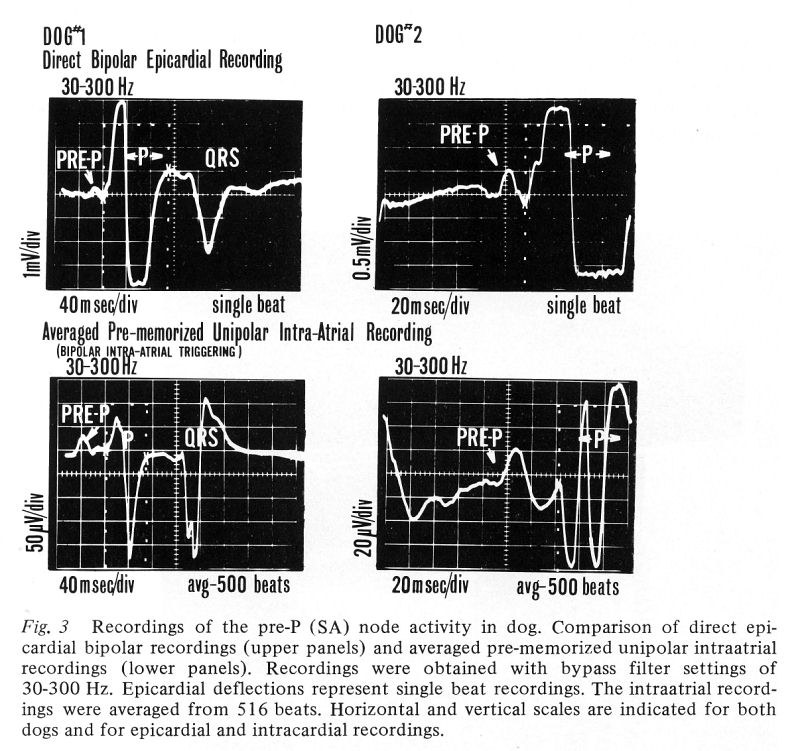
The SA (pre-P) potential recordings obtained simultaneously in dog
experiments (5 dogs) from the epicardial electrodes sutured in the
area of the SA node and from the averaged unipolar intraatrial
recording showed excellent correlation.
Pre-memorized averaged intraatrial recordings were obtained in humans
(5 patients) during right heart catheterization using a multipolar
electrode catheter. The recordings in both experimental animals and
humans revealed double spiked, preatrial potentials of 40-50 μV and 1.0-1.5
μV amplitude, respectively, usually located 30-60 msec
before the right atrial spike (or beginning of atrial activity). These
potentials are assumed to represent the activity of the SA node.
Electrophysiological as well as clinical applications of this method
for recording of SA node activity require further study, but appear
promising in evaluation of sinoatrial node function abnormalities.
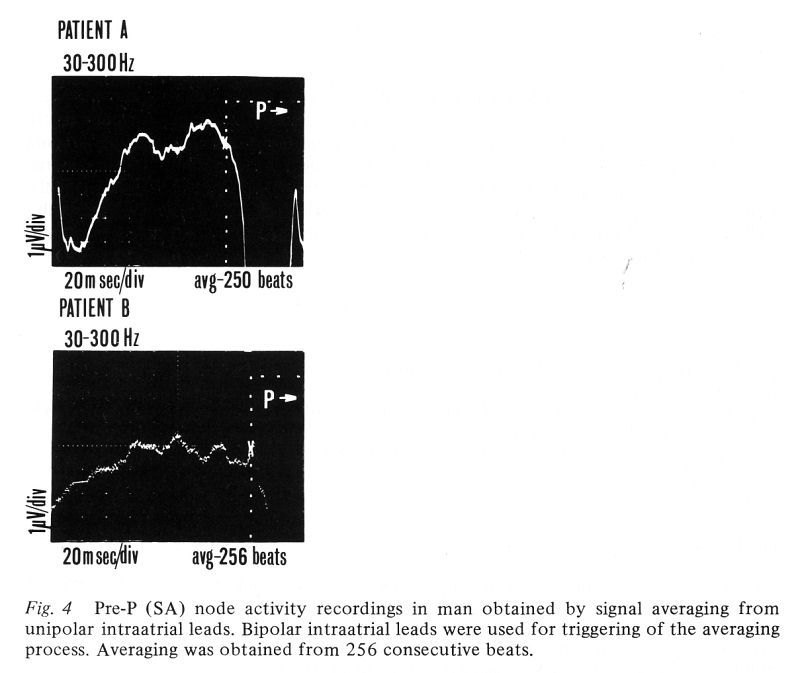
Other publications:
Pre-P
(Sino-Atrial Node Region) Activity Recording from the Right Atrial
Cavity by Signal Averaging*.
MARIUSZ J.
STOPCZYK, WALDEMAR J. WAJSZCZUK,
RYSZARD J. ZOCHOWSKI, MELVYN RUBENFIRE.
Pacing Clin
Electrophysiol.
1979 Mar;2 (2):156-61.
*Presented in part at the Vth International Symposium on Cardiac
Pacing. Tokyo, Japan. March 14–18, 1976.
Copyright 1979 Official journal of the International Cardiac
Pacing and Electrophysiology Society
(http://www.labmeeting.com/papers/author/wajszczuk-w)
http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/journal/120057221/abstract?CRETRY=1&SRETRY=0
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1540-8159.1979.tb05195.x/abstract
A mobile instrumentation
and noninvasive method developed recently for external His bundle
recording and employing the signal averaging technique was applied for
intra-atrial recording of the pre-P (sino-atrial node region)
activity. Recordings were obtained in ten anesthetized dogs and five
patients at the time of right heart catheterization. A bipolar
intra-atrial lead was used for triggering of the averaging process and
a unipolar intra-atrial lead was used for signal recording. Direct
bipolar epicardial recordings were obtained for comparison from the
sino-atrial (S-A) node area in experimental animals. In animals
studies, the averaged intra-atrial recording showed 30 μV amplitude deflections beginning 40-45 ms prior to the
onset of P wave and were preceded by a slow rise and lower frequency
and amplitude deflections arising 60-70 ms earlier. There was good
correlation between the pre-P activity recorded intra-atrially and
from the epicardium. Deflections of similar configuration but smaller
amplitude (1 μV) were recorded
in human studies. They preceded the onset of large atrial activity
deflections (P wave) in the reference electrocardiogram by 40-80 ms.
The exact source of these pre-P activity potentials has not been
definitely established, but they appear to originate from the S-A node
region, based on their similarity to the direct epicardial recordings
and time relationship to the preceding T and following P wave.
Experimental Correlations
Summary
The purpose of this
communication is to review the experimental models and techniques,
which have been utilized in our laboratory to identify the individual
deflections in external (pre-triggered and signal averaged) recordings
from the cardiac conduction system.
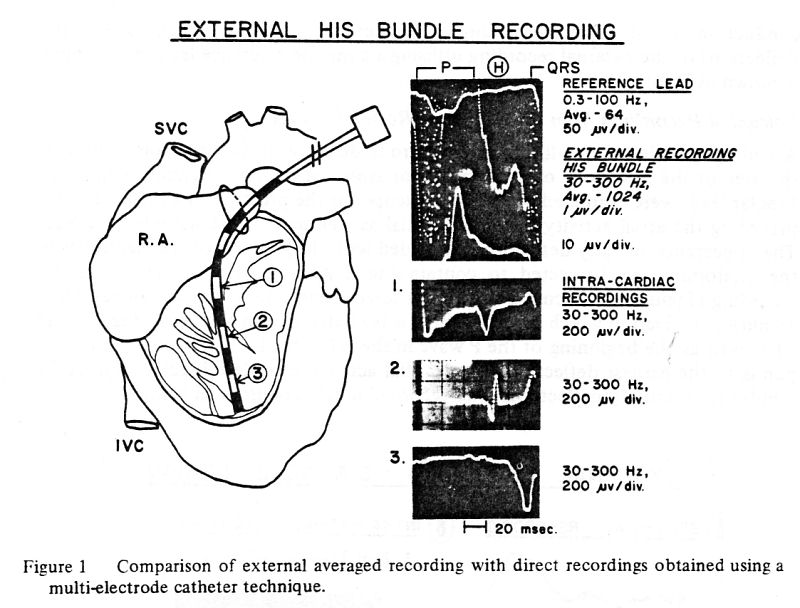
1. Electrode catheter recordings from the right
ventricular cavity – 5 dogs. (Figure 1).
A multi-electrode catheter was
introduced through a small incision in the right atrial appendage and
advanced to the apex of the right ventricle. The catheter was
gradually withdrawn towards the tricuspid valve. The signals from the
distal pair of electrodes (10 mm apart) were observed on the
oscilloscope. Bipolar recordings were obtained when His bundle
deflections were noted and the position of the electrodes was verified
by external palpation. Direct recordings were correlated with the
external averaged recordings obtained prior to thoracotomy and after
temporary closure of the chest after completion of the direct
recording.
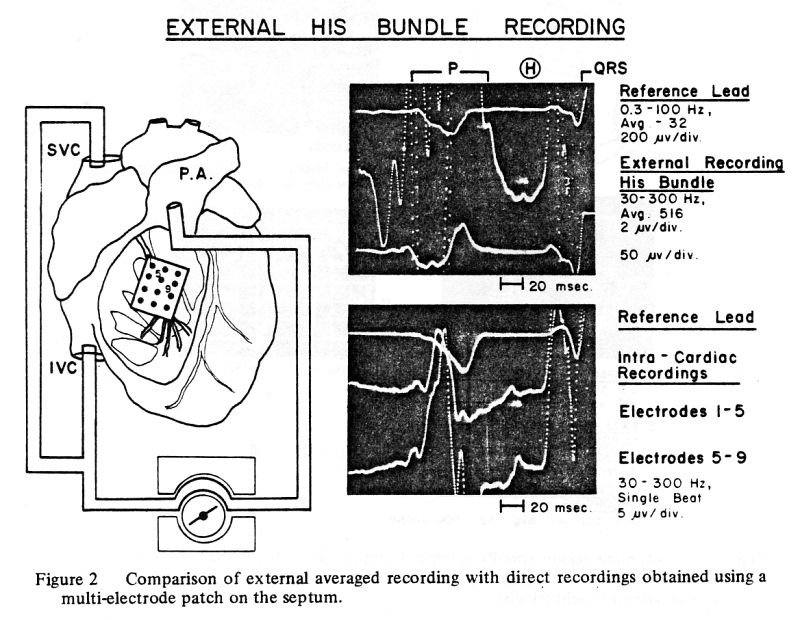
2. Endocardial recordings with multi-electrode
patch – 10 dogs. (Figure 2).
A multi-electrode patch (15 x
30 mm) with 12 silver electrodes (0.5 mm in diameter) mounted in
dacron mesh in three rows of four electrodes (4 – 5 mm apart) was
used. Implantation of the electrode patch required temporary
cardiopulmonary bypass. The electrode wires were brought outside the
chest, which was then closed with loose sutures. The dogs were
observed for 30-45 minutes to allow stabilization. Bipolar leads from
various combinations of electrodes were examined on the oscilloscope
and recordings were obtained from the pairs of electrodes, which
displayed the cardiac conduction system potentials. They were then
correlated with the external recordings.
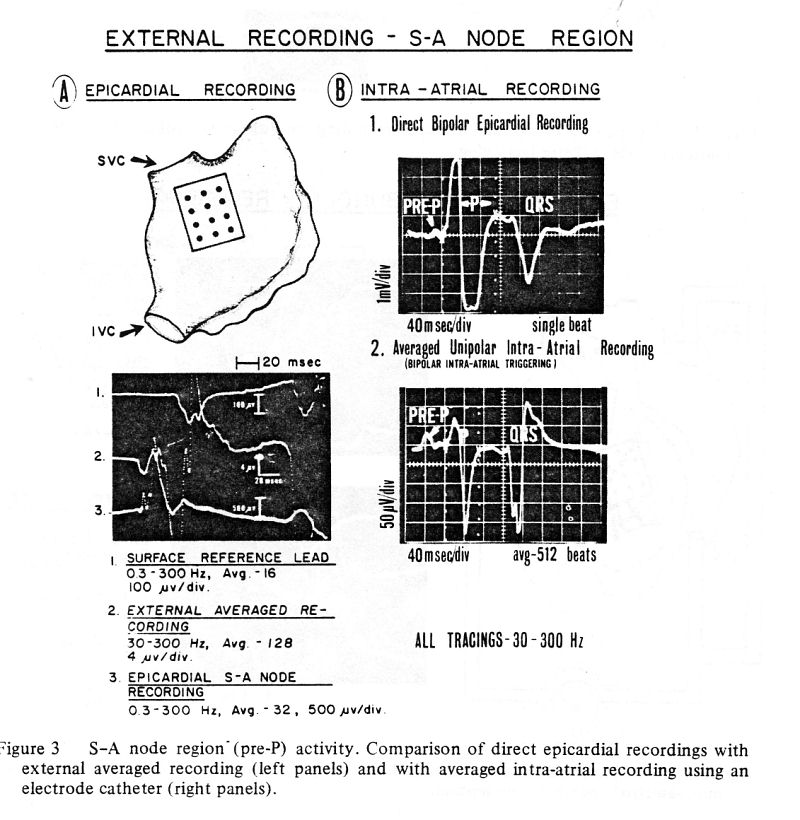
3. Epicardial recordings from the S-A node
region – 5 dogs. (Figure 3).
A multi-electrode patch
(described above) was sutured in the area of the S-A node over the
posterior aspect of the right atrium. Bipolar leads were examined in
various combinations for the presence of earliest activity preceding
the atrial activity in the reference leads and recordings were
obtained from the pairs of electrodes showing this early activity. The
appearance of these early deflections coincided with the position of
the electrodes in the anatomic area suspected to contain the S-A node.
Similar early activity deflections were seen in all experimental
animals. (Figure 3A).
4. Intra-atrial recordings
from the S-A node region – 10 dogs. (Figure 3).
A multipolar electrode
catheter was advanced in anesthetized dogs via the femoral vein to the
right atrium and positioned under gentle palpation along the junction
of the superior vena cava and the right atrium. The catheter tip
containing the terminal pair of electrodes was located in the vicinity
of the presumed site of the S-A node. A unipolar lead from one of the
electrodes of the pair was used for signal recording and a bipolar
lead from the same pair of electrodes was used for triggering.
For comparison, direct bipolar
epicardial recordings were obtained from the region of the S-A node
utilizing the electrode patch (described above) or electrode strips
containing silver electrodes with an interelectrode distance of 2-3
mm. The early low voltage deflections of averaged intra-atrial
recordings corresponded closely to the earliest activity deflections
recorded with the epicardial electrodes. It is assumed that both these
deflections represent activation originating from the region of the
S-A node.
Examples of the recordings are shown below:
Publications listed below summarize our investigative work on this
subject and are reproduced in their entirety:
1/ Non-invasive studies of cardiac conduction system.
W.J.Wajszczuk, M.S. Moskowitz, T. Bauld, T. Palko, J. Przybylski, P.
Dabos, R. Weiss, M. Stopczyk, R. Żochowski, M. Rubenfire. Proceedings
of “BIOSIGMA 78”, International Conference on Signals and Images in
Medicine and Biology, Paris, April 24-28, 1978. Session C.IV:
Non-aggressive methods for data acquisition, Communication C.IV.2 -
see
2/ NEW DEVELOPMENTS AND EXPERIMENTAL OBSERVATIONS ON EXTERNAL (NON-INVASIVE)
RECORDING FROM THE CARDIAC CONDUCTION SYSTEM * W.J. WAJSZCZUK,
J. PRZYBYLSKI, T. PAŁKO, M. WORPELL, TH. BAULD AND M. RUBENFIRE.
Electrocardiology '81, Budapest, Hungary, 1981. Z. Antaloczy, and I.
Preda (eds.)., pp. 89-94. - see
Presentations
PAPERS SUMMARIZED OR REPRODUCED ABOVE WERE PRESENTED AT THE NATIONAL
AND INTERNATIONAL MEETINGS HELD IN:
1. TOKYO, JAPAN – 1976. Vth International Symposium on
Cardiac Pacing, March 14–18, 1976.
2. SAN FRANCISCO, CA – 1977. AAMI, 12TH Annual Meeting,
March 13-17, 1977.
3. PARIS, FRANCE – 1978. “BIOSIGMA 78” – International
Conference on Signals and Images in Cardiology, April 24-28, 1978.
4. GLASGOW, SCOTLAND – 1978. 5th International Congress
on Electrocardiology, September 5-8, 1978.
5. COLOGNE, GERMANY – 1981. International Symposium on
the Signal Averaging Technique in Clinical Cardiology, May 7-9, 1981.
6. BUDAPEST, HUNGARY – 1981. 8TH International Congress
on Electrocardiology, September 1-4, 1981.
At this point the
research project was terminated because of the exhaustion of funds and
inability to obtain further financial support!
Suggestions (and plans) for further continuation
of research on this topic:
1/ further development of a method for three-dimentional (vectorial)
representation of the activation of the cardiac physiological
pacemaker and conduction system;
2/ experimental re-creation and study of various forms of the
conduction system abnormalities;
3/ collection of clinical material representing various conduction
abnormalities and development of the diagnostic criteria;
4/ can the A-V node activation potentials be identified (separated) in
the external recordings?
His bundle cardiography - US Patent 4261369
US Patent Issued on
April 14, 1981
Estimated Patent Expiration Date: February 14, 1999
http://www.patentstorm.us/patents/4261369/fulltext.html
Abstract
A non-invasive technique for monitoring the atrioventricular His
bundle electrocardiogram and recording the same on a strip chart
recorder in parallel real time with a conventional surface ECG signal.
The preferred embodiment of the His bundle circuitry includes
separately adjustable highpass and lowpass filters in the frequency
range of 30 to 600 Hz, and a variable gain amplifier for in situ
empirical adjustment to patient and environmental conditions.
|